Tutlayt Talmant
Talmant (assaɣ ayman: Deutsch) d yiwet n tutlayt Taǧermant tutrimt igan d yiwen n ufurk seg twacult n tutlayin tihendurupyin, Talmant tettumeslay s talɣa tagejdant deg Uruppa talemmast anda i tga d tutlayt tamaddudt n Tegduda n Lalman tadukklant d tegduda Tutrict d umazan n Liechtenstein akken daɣen i tga d yiwet seg kuẓ (4) n tutlayin tinamurin n Teswist d yiwet daɣen seg 3 n tutlayin timaddudin n tdukt n Luxembourg yakk d yiwet seg tutlayin timaddudin n Tgelda n Biljik (Tamɣiwent yessawalen Talmant n Biljik) yakk d tutlayt tamaddudt deg tama n unẓul n Tyrol id yezgan deg ugafa n tegduda n Italy, yakk d tutlayt n tadersi Jutland n unẓul yeṭṭafaren tamurt n Danmaṛk
Tutlayin tiǧermanin n umalu n iden am Tefrikanist d Tehullandit d Tegnizt d Tefrist d Telmant taddayt d Tyidict d gid-ak yakk yettemcabin s waṭas ar Telmant akken daɣen yella kra wemcabi s tfesniwin yemgaraden yakk d Tdanict d Tnerwijt d Teswidt yeṭṭafaren afurk agafay n tutlayin tiǧermanin
Talmant d tutlayt Taǧermant tis snat deg wemdan n imsawalen seld n Teglizt
| Talmant | |
|---|---|
| Deutsch | |
| Abdar | dɔʏtʃ |
| Aẓaran deg | Asegder arakal i yemsawalen n Telmant |
| Tamnaḍt | Lalman d tmura n iden |
| Azdar |
Imsawalen s Telmant |
At tutlayt tayemmat |
90 million (2010)[1] to 95 million (2014)[2] L2 speakers: 10–15 million (2014)[2][3] |
Talɣiwin tizikanin | |
Standard forms | |
|
Agemmay Alatin (German alphabet) German Braille | |
|
Signed German, LBG (Lautsprachbegleitende / Lautbegleitende Gebärden) | |
| Addad amaddud | |
| Tamaddudt deg |
Several international institutions |
| Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by |
No official regulation |
| Ingalen n tutlayt | |
| ISO 639-1 |
de |
| ISO 639-2 |
ger (B) deu (T) |
| ISO 639-3 |
Variously:deu – Germangmh – Middle High Germangoh – Old High Germangct – Colonia Tovar Germanbar – Bavariancim – Cimbriangeh – Hutterite Germanksh – Kölschnds – Low GermanTuccḍa n temsisɣelt: Balise <ref> incorrecte : les références sans nom doivent avoir un contenu.sli – Lower Silesianltz – LuxembourgishTuccḍa n temsisɣelt: Balise <ref> incorrecte : les références sans nom doivent avoir un contenu.vmf – Mainfränkischmhn – Mòchenopfl – Palatinate Germanpdc – Pennsylvania Germanpdt – PlautdietschTuccḍa n temsisɣelt: Balise <ref> incorrecte : les références sans nom doivent avoir un contenu.swg – Swabian Germangsw – Swiss Germanuln – Unserdeutschsxu – Upper Saxonwae – Walser Germanwep – Westphalianhrx – Riograndenser Hunsrückischyec – Yenish |
| Glottolog |
high1287 High Franconian[5]uppe1397 Upper German[6] |
| Linguasphere |
|
 | |
Talmant d yiwet gar tutlayin timadlanin timeqranin acku tga d tutlayt tayemmat i wugar n 100 n imelyan n yemdanen deg umadal, akken i tga d tutlayt tamezwart deg tiddukla n Turuft akken daɣen i tga d tutlayt tis snat (s tezfi yakk d Tefrensist) seld n Teglizt ayen ara ad tt-yeǧǧen d tutlayt tis snat deg tiddukla n Uruppa seld Taglizit
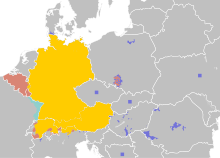
Asegder arakal
ẓregUruppa
Talmant tettusexdem deg ansa amezwar deg Lalman anda tga d tutlayt tayemmat n 95% n imezdaɣ-is, 89% deg Tutrict, 65% di Teswist akken i tga d tutlayt n tigti deg Liechtenstein, akken daɣen i tella Telmant d tutlayt n tdersi deg kra n tamiwin d igezduyen n Ṭelyan d Danmaṛk, Akken daɣen i llant kra n timɣiwanin yettmeslayen s Telmant deg kra n imuren n tmurt n Ččik d Hungaria d Puḷunya d Rumanya yakk d kra n tmura n iden ur nli (ur nesɛi) tilisa s Lalman am Kazaxistan d Qubrus d Sirbya
Deg uzaɣar n Uruppa
Amzegraw ameqran yakk n imsawalen s Telmant deg uzaɣar n Uruppa d win yellan deg Iwunak Yeddukklen n Marikan d Kanada d Brazil d Tarjentint anda imelyan n Ilmanen gguǧǧen ar tmura ayyi seg 200 n iseggasen-a yezrin maca tura azgen ameqran n warraw-nsen ur ttmeslayen ara Talment
Imeslayen imezdayen yakk d Teglizt
ẓregAẓaṛ n tutlayt Taglizit yettuɣal ar Telmant anda iminigen Ilmanen ddmen tutlayt-a ar Bṛitanya
Asuffeɣ n Telmant ar umadal
ẓregTiwelhiwin
ẓreg- ↑ Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2010" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2010), in Nationalencyklopedin
- ↑ 2,0 et 2,1 Ammon, Ulrich (2014). Die Stellung der deutschen Sprache in der Welt (in Talmant) (1st ed.). Berlin: de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-019298-8. Retrieved 24 July 2015.
- ↑ Tuccḍa n temsisɣelt: Balise
<ref>incorrecte : aucun texte n’a été fourni pour les références nomméeseurobarometer - ↑ "Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung – Über den Rat". Rechtschreibrat.ids-mannheim.de. Retrieved 11 October 2010.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "High Franconian". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Alpine Germanic". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.